2022-11-09
LED is also known as light-emitting diode (LightEmitting Diode), belongs to the semiconductor components, since 1962, the United States General Electric Company developed the world's first practical application of red LED, LED has entered the full color era. Diode, in the P-N diode ends plus the downward bias, when the current through, electrons and holes flow to the joint surface will release energy and light.
LED itself is a monochromatic light source, now with the improvement of light efficiency and the emergence of blue LED, its applications are gradually diversified, from the earlier low-power power indicator evolved into LED backlight modules and LED lighting ... and other high-power applications. LED is known as the new light source of the 21st century, it has high efficiency, long life, energy saving, not easy to break, environmental protection without The advantages of traditional light sources such as mercury can not be compared with it, in the energy saving and carbon reduction and environmental awareness is still emerging, coupled with the energy policies announced by governments one after another (for example: the U.S. "Energy Independence and Security Act" enacted in 2007 proposed incandescent lamp ban schedule, Japan's 2010 revision of the "Energy Fundamental Plan" proposed carbon reduction goals), making a large proportion of domestic electricity consumption Lighting", which accounts for a large proportion of domestic electricity consumption, has become one of the items encouraged to be replaced. Energy trends, government decrees and LED light-emitting characteristics of the three multiplier effect, prompting the LED lighting industry to flourish, but also to attract domestic / foreign manufacturers for LED upstream, midstream and downstream industries to invest.
LED as all electronic parts in general, in the use or operation of the process will produce heat and temperature rise phenomenon, if ignore the problem of heat dissipation, will lead to LED due to high temperature and early burn results. LED lamps and lanterns design more complex than traditional lamps and lanterns, including optical, institutional, electronic and heat dissipation, of which "heat dissipation" is particularly important, because the current conversion rate of high power LED lamps and lanterns only 20% will be converted into light The remaining 80% will be converted into heat, if the heat can not be exported outside the lamp, will not be able to achieve the claimed 50,000 hours of life of the LED light source, while the heat will affect the LED luminous efficiency, resulting in serious light failure and destruction of the lamp tragedy.

The thermal design of LED lamps and lanterns
LED luminous efficiency and life is closely related to the working temperature, showing an inverse relationship, the following chart for the United States CREE released the LED life report, the temperature for every 10 ℃ life will be extended by 2 times and luminous flux increased by 3% ~ 8%.
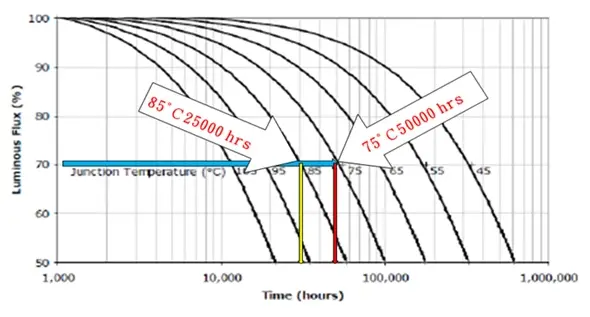
Due to the development of high-power LED technology, LED lamps and lanterns are facing severe challenges of thermal management and heat dissipation design, because the increase in temperature will not only cause a decrease in brightness, when the temperature exceeds 100 degrees Celsius will accelerate the deterioration of the lamp body and packaging materials. Therefore, in addition to the heat dissipation technology of the LED package components themselves, the heat dissipation and thermal conductivity design of the LED luminaire is the biggest key to maintain the life of the luminaire.
LED applications in outdoor lighting, its thermal design compared to other LED end products (for example: LED backlight panels, LED automotive lighting ... etc.) more complex and diversified, because the operating environment of LED lamps and lanterns will be more demanding because of temperature changes, the amount of sand and dust, humidity ... and other factors. LED street lights, for example, to be able to work for a long time in the outdoor environment, must not only meet the requirements of safety regulations (for example: UL, CE ...), but also to overcome the stability of optical properties (such as, light decay changes), sand and dust invasion, bird droppings, airborne colloidal suspended substances and water siphoning phenomenon caused by the waterproof and dustproof problems and other reliability and harsh environmental tests.
In the lamp design, by the LED pistons, LED chip substrate, chip packaging, line design, system circuit board, heat dissipation fins to the lamp housing again and again are testing the LED industry up, middle and downstream of the R & D capabilities. Traditionally used for indicator LEDs are mostly shell-type structure, which is surrounded by insulating epoxy resin (epoxy) for packaging, so the heat generated by the LED grains mainly by the two metal wires below to conduct the way to the direction of the system circuit board dissipation. However, when the LED crossed into the field of lighting, more than 1W high power LEDs become the mainstream, but also in order to increase the heat transfer area, the LEDs for lighting purposes to adopt a flat package, so that the LED chip substrate and the system board can have a larger paste area.
At present, the common LED chip substrate is ceramic substrate, its good heat dissipation, low coefficient of expansion and other characteristics to reduce the thermal stress due to deformation, followed by heat resistance, moisture resistance, insulation and other advantages, so the ceramic substrate has become a common heat dissipation material for high-power lighting LED chip substrate. Ceramic substrates are currently divided into three categories: (1) alumina (Al2O3), (2) low-temperature co-fired ceramics (LTCC), (3) aluminum nitride (AlN), of which AlN is the best thermal conductivity, but the highest technical hurdle, so AlN is mostly used for more than 3W LED products, while Al2O3 is used in the range of 1W ~ 3W, LTCC is suitable for large size high-power, small size small LTCC is suitable for large size high power and small size small power LED products. Take CreeXLamp LED series as an example, that is, adopt ceramic base to optimize heat dissipation ability.

1. The classification of the thermal substrate and expansion, thermal conductivity is introduced.
In the packaging, can be used to hit the wire, eutectic or over crystal three ways to connect the pads and LED heat sink substrate, hit the wire is connected to the LED pads and chip substrate by metal wire, the heat generated by the pads can only be conducted by wire, heat dissipation performance is limited by the material and slender geometry of the wire, so the heat dissipation performance is highly restricted, compared to eutectic, over crystal bonding method, significantly reducing the length of the wire and In contrast, the eutectic and overmolded bonding method significantly reduces the length of the wire and increases the cross-sectional area of the wire to enhance the thermal conductivity.
In terms of line improvement, some manufacturers have introduced high-voltage LED products, the principle is to connect many low-power LEDs in series to get high voltage, low current products. High-voltage LEDs are mostly used in bulbs, lamps, projection lamps and other lighting products with limited space, which can reduce the difficulty of the control line arrangement. Compared with general LEDs, the driving current of high voltage LEDs is smaller, and the heat generated is also relatively less, which can avoid falling into the vicious cycle of "temperature rise, impedance fall, current increase, heat increase, temperature rise" and can design LED lamps with better system stability.
After the introduction of the LED chip substrate, then mentioned the same in the transfer of heat has a heavy responsibility for the system circuit board, LED chips by welding and system circuit board for linking, the heat generated by the pistons are also conducted by the chip substrate to the system circuit board, currently commonly used with high thermal conductivity of the metal core PCB (Metal CorePCB; MCPCB), although the aforementioned has mentioned ceramic MCPCB is composed of a 3-layer structure, from top to bottom are the conductive line layer, high thermal conductivity insulation layer and metal substrate, where the material of high thermal conductivity insulation layer must be carefully selected, if the use of high expansion coefficient of the material, the insulation layer is easy to expand at high temperatures and the metal substrate. Insulation layer is easy to expand at high temperatures and produce cracks, cavities, but the air into the MCPCB, forming additional thermal impedance, reducing the efficiency of thermal conductivity, some manufacturers will spray ceramic thermal paint between the thermally conductive insulation layer and the metal substrate, which can improve the insulation impedance of the insulation layer, save the cost of materials for multi-layer thermal adhesive and strengthen the thermal capacity of the MCPCB; the bottom layer of the metal substrate is mostly made of aluminum alloy, using Aluminum alloy better heat dissipation characteristics to achieve the purpose of heat transfer.

The back end of the system board combined with the cooling system for heat dissipation, cooling system can be divided into active cooling and passive cooling, active cooling includes fan forced cooling and magnetic jet cooling, passive cooling includes natural convection cooling, loop heat pipe cooling, which will be introduced one by one as follows.
1. Fan forced cooling.
Fan forced heat dissipation as the name suggests is the fan to generate air convection, the hot air out of the lamp body outside the heat dissipation, the use of fan forced heat dissipation can be very effective in the computer, air conditioning and automotive fans to force heat dissipation
2. Electromagnetic Jet Heat Dissipation.
Electromagnetic jet heat dissipation does not use fan blades to generate airflow, its structure is a hollow cavity with a thin film, which uses electromagnetic or piezoelectric actuators to oscillate the film at a frequency of 100-200 times per second, prompting the film to oscillate up and down, with the up and down displacement of the film, the air will flow into the hollow cavity and then ejected, the airflow will drive the surrounding air to produce vortex phenomenon, strengthening the air convection capacity, has been It has been applied to GE 27W Energy SmartLED bulb lamp.
3. Natural convection heat dissipation.
Natural convection heat dissipation is through direct contact between the heat sink (e.g., heat sink fins, lamp housing, system circuit board, etc.) and the air, the air around the heat sink becomes hot air due to heat absorption, and then the hot air rises and the cold air falls, naturally driving the air to produce convection, achieving the effect of heat dissipation. With the introduction of high power lamps and lanterns, the use of natural convection heat dissipation requires a larger surface area for heat dissipation, so fins are installed on the back of the lamps and lanterns to provide a larger area for heat dissipation and strengthen the effect of convection heat dissipation.
Although the use of fins increases the heat dissipation effect, but also increases the overall weight and cost of the lamp, but also adds to the risk of safety hanging pole-type lamps, in addition, LED lamps often face dust accumulation and other problems, once after a long time of use, too much dirt, dust accumulated in the fins, will weaken the ability to dissipate heat, compared to some of the industry choose to design the fins with the lamp luminous surface in the same direction (down Heat dissipation), completely avoid the problem of dust accumulation
4. Loop heat pipe heat dissipation.
This heat dissipation method is through the circulating heat pipe, the two ends of the loop tube for the system circuit board (heat source) and heat sink, the inside of the loop tube is filled with working fluid, and equipped with evaporator, its working principle is: when the system circuit board heat, the working fluid at the heat source to absorb heat, through the evaporator into a gas, using the characteristics of the rapid movement of gas, the heat at the heat source can be quickly conducted Therefore, the circuit heat pipe heat dissipation only solves the heat conduction problem and cannot effectively achieve the "heat dissipation" function.
Introduction of heat dissipation system for lamps
In the design of lamps and lanterns, the heat sink fins and outer housing are exposed to air, and in order to avoid oxidation, they are often anodized. In recent years, some manufacturers have introduced soft ceramic heat sink paint to replace the anodizing process, and claim that its thermal resistance value is close to that of metal, which can accelerate the performance of heat conduction.
Up to now, the above discussion are heat conduction and heat convection two ways, currently there are manufacturers claim that its ceramic heat dissipation substrate can use far-infrared type will heat radiation dispersion, long-distance heat transfer, and claim that can be used to replace the LED chip substrate back end of the heat-conducting metal (heat dissipation fins, metal lamp housing), to achieve successful heat dissipation and reduce the weight of the light effect, this technology of heat dissipation performance if true as the manufacturer said If the heat dissipation performance of this technology is true to the manufacturer's claims, it will also bring significant progress to the heat dissipation design of LED lamps.

Conclusion
The thermal design of some commercially available LED lamps and lanterns tends to overlook some details, such as ignoring the uniformity of heat transfer, i.e., the temperature distribution of the heat sink fins is seriously uneven, resulting in a part of the fins having limited effect on heat dissipation, or even not playing a role in heat dissipation. Some design errors will bring danger, especially LED street lights are usually installed in 8 to 12 meters pole height, if the radiator center of gravity is not well designed, may lead to excessive weight and wind resistance, increased danger, when encountering typhoons or earthquakes will likely lead to serious accidents.
Lighting entrepreneurs once said: "As a high-tech energy-saving lighting industry practitioners must recognize that good heat dissipation of LED lamps and lanterns (including heat conduction, temperature uniformity, heat exchange ... etc.) must be based on the complex hard theory of the foundation of heat transfer, must face the performance of LED street lights, must have scientific data and theory to support, perfect system design methods for The approach, good manufacturing process as the basis, and finally to the third impartial unit of the test report as the basis, so as not to repeatedly occur light recession goods hinder the development of the industry vicious circle ".
How to fight for the market at the same time prudently assess their own product quality, research and development and process capabilities, good LED lamps and lanterns heat dissipation design to withstand the test of time and the environment, are the focus of strict self-regulation of enterprises must be.
-THANKS FOR WATCHING-
Lighting Industry Exports To North America Market Major Certification